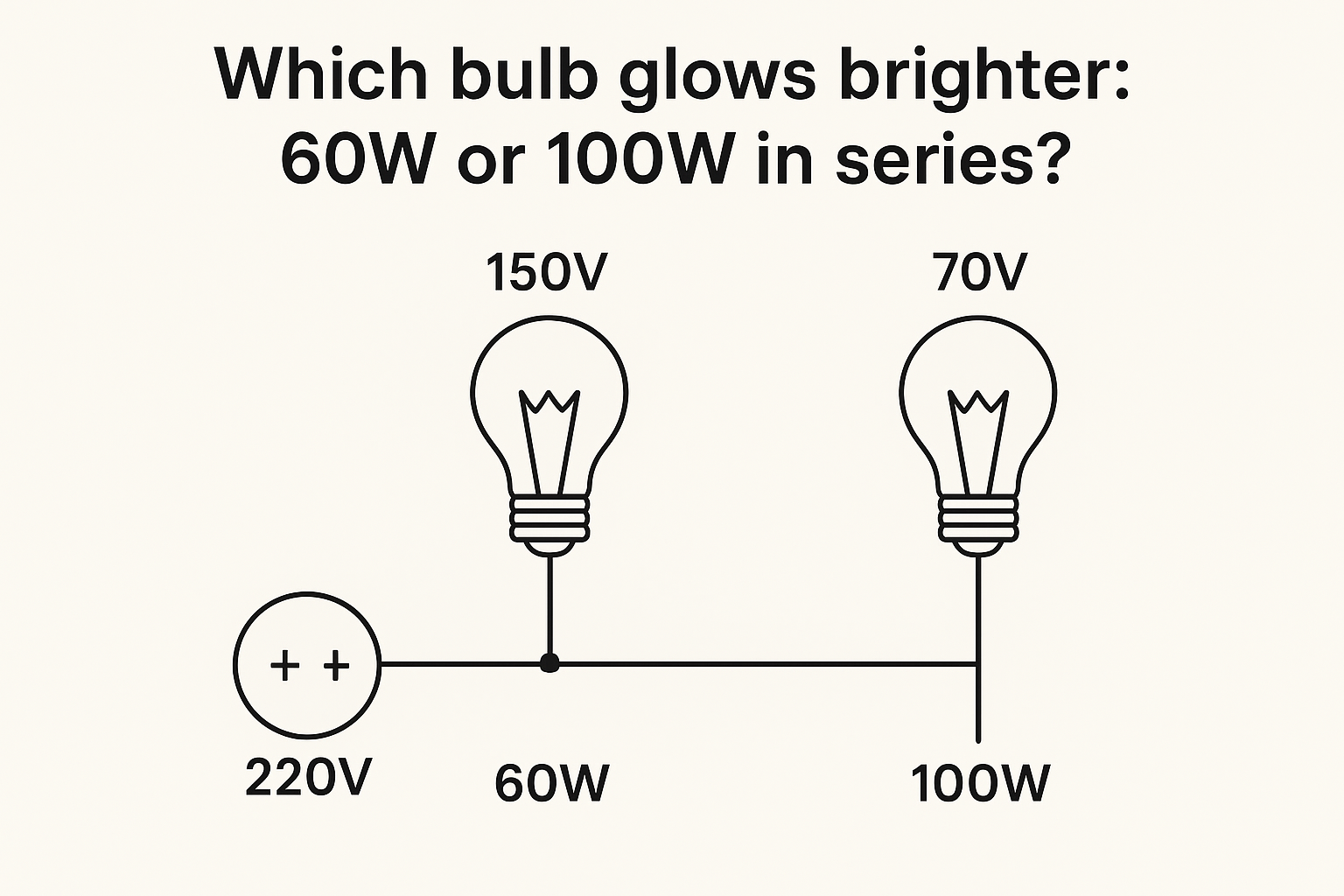
This question is a classic basic electronics one, always asked in interviews and at examinations. At first, many might say the 100-W bulb would glow brighter because of its higher power rating. But anger would surely surprise you when told the actual answer.
Understanding Bulb Power Ratings
- A 60-Watt bulb exactly implies its power rating is 60 watts when the same is associated with its indicated rated voltage (220V).
- A 100W bulb means it consumes 100 watts of power when connected directly across 220V.
So, the wattage rating tells us about the resistance of the filament at the rated voltage:
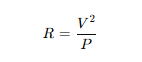
For 220V supply:
- Resistance of 60W bulb:
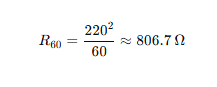
- Resistance of 100W bulb:
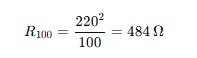
So the 60W bulb has higher resistance than the 100W bulb.
Bulbs Connected in Series
When connected in series to the 220V supply:
- The same current flows through both bulbs.
- The voltage divides across them in proportion to their resistance.
Since V=I×R, the bulb with higher resistance will get more voltage.
- Voltage across 60W bulb (higher resistance) > Voltage across 100W bulb (lower resistance).
Power Dissipation in Series
The brightness of a bulb depends on the power it actually consumes in the circuit:
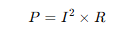
- Because the current is the same, the bulb with higher resistance will dissipate more power.
- That means the 60W bulb will glow brighter than the 100W bulb when connected in series.
Final Answer
When a 60W and 100W bulb are connected in series across a 220V supply, the 60W bulb glows brighter because it has a higher resistance and thus consumes more power in the series circuit.
✅ Key Takeaway:
- In parallel connection → The 100W bulb glows brighter (as expected).
- In series connection → The 60W bulb glows brighter (opposite of what many assume).